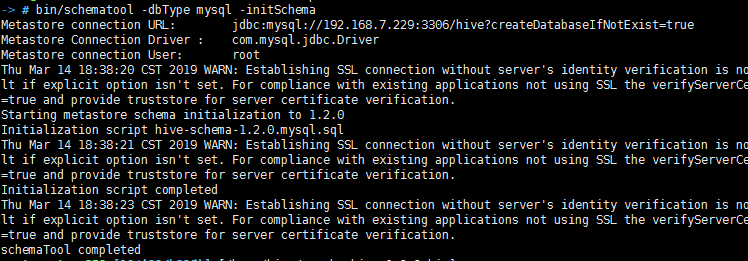
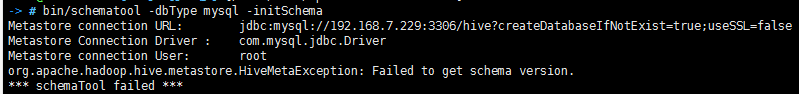
安装UnixODBC
YUM 直接安装
1、yum install unixODBC-devel
下载包安装
1 | tar zxvf unixODBC-2.3.0.tar.gz |
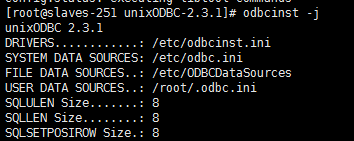
安装MYSQL的驱动文件
yum -y install mysql-connector-odbc
cat /etc/odbcinst.ini # 查看驱动程序信息
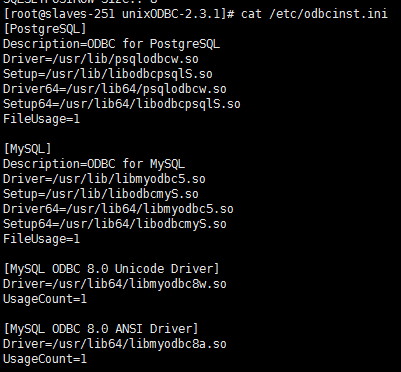
配置ODBC驱动
vim /etc/odbc.ini
1 | [mysql_229] |
Driver 填写驱动程序信息中每种驱动的描述
测试ODBC连接情况
isql mysql_229 -v # 连接某个数据源

strace isql mysql_229 -v # 跟踪错误信息